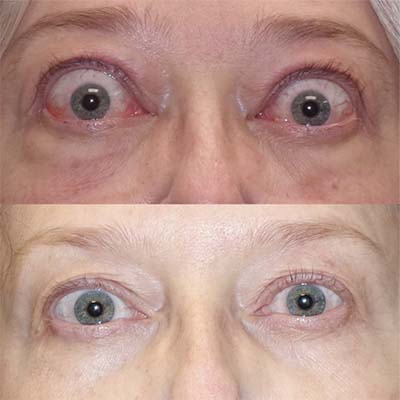
Thyroid eye disease (TED) is a complex autoimmune condition that affects the tissues around the eyes. It often leads to symptoms like swelling, redness, bulging eyes, double vision, and light sensitivity. Managing these symptoms is essential for improving the patient’s quality of life and preventing long-term complications.
While surgical interventions are sometimes necessary for severe cases, many patients benefit from non-surgical thyroid eye disease treatment options. These approaches aim to alleviate symptoms, control inflammation, and slow disease progression. Let’s explore the most effective non-surgical treatment options available for TED.
Corticosteroids Treatments
Corticosteroids are a cornerstone in the management of TED, particularly during the active phase of the disease when inflammation is at its peak. These medications help reduce swelling and inflammation around the eyes. Corticosteroids can be administered in various forms, including oral tablets, intravenous infusions, or injections.
Intravenous steroids are often preferred for their rapid and potent anti-inflammatory effects. However, long-term use of corticosteroids may lead to side effects such as weight gain, mood changes, or an increased risk of infections, so careful monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential.
Tepezza (Teprotumumab)
Tepezza is the first FDA-approved medication designed explicitly for thyroid eye disease. It targets and inhibits the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), which plays a key role in the inflammatory process associated with TED. Clinical trials have shown that Tepezza can significantly reduce eye bulging (proptosis), double vision, and other symptoms of TED.
Lubricating Eye Drops and Ointments
Dry eyes are a common complaint among TED patients. Artificial tears and lubricating eye ointments can relieve dryness, irritation, and the gritty sensation often associated with the condition. Preservative-free eye drops are generally recommended to minimize the risk of further irritation.
For more severe cases, gel-based lubricants or nighttime ointments may be beneficial. These products help maintain moisture on the eye surface, improving comfort and reducing the risk of corneal damage.
Prism Glasses for Double Vision
Double vision, or diplopia, is a frequent symptom of TED due to misalignment of the eye muscles. Prism glasses can help correct this issue by realigning the visual fields and allowing the patient to see a single image. These specialized lenses are customized to the individual’s needs and can significantly improve daily functioning.
For some patients, wearing an eye patch over one eye may also temporarily relieve double vision, although this approach is generally used as a short-term solution.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Beyond corticosteroids, other anti-inflammatory medications can help manage TED. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can help reduce mild inflammation and discomfort. However, these are typically used as supplementary treatments rather than primary therapies for TED.
In some cases, immunosuppressive drugs like mycophenolate mofetil or methotrexate may be prescribed to help control the autoimmune response driving the disease. These medications require careful monitoring due to their potential side effects, but they can effectively reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a less commonly used non-surgical option for TED but can effectively reduce inflammation and control symptoms in some instances. This treatment involves targeting the tissues around the eyes with low-dose radiation to decrease the activity of immune cells causing inflammation. Radiation therapy is often combined with other treatments, such as corticosteroids, for a synergistic effect.
While it can benefit some patients, the potential risks and side effects should be thoroughly discussed with a specialist, including damage to surrounding tissues.
Lifestyle Modifications for Thyroid Eye Disease (TED)
Simple lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing TED symptoms. For example:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for TED progression and can reduce the effectiveness of treatments. Quitting smoking can help improve outcomes and slow the disease.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate autoimmune conditions, including TED. Incorporating relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress.
- Protect Your Eyes: Wearing sunglasses with UV protection can shield your eyes from sunlight, wind, and other environmental irritants. Additionally, using a humidifier in your home can help prevent dry eyes by maintaining adequate moisture levels in the air.
Dietary Adjustments
A healthy, anti-inflammatory diet can support overall eye health and complement other TED treatments. Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, which can help reduce inflammation.
Fresh fruits and vegetables, mainly those high in antioxidants like vitamin C and beta-carotene, can promote eye health. Limiting processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats may help control inflammation and improve symptoms.
Physical Therapy for Management of Eye Muscles
For patients experiencing restricted eye movement or difficulty focusing, physical therapy specifically designed for the eye muscles may help. Guided exercises can improve muscle strength and coordination, reducing discomfort and improving overall eye function. This non-invasive approach can be an effective adjunct to other treatments, particularly for those with persistent double vision or stiffness in eye movement.
Emotional Support and Counseling
Living with TED can be emotionally challenging due to its impact on appearance and daily functioning. Seeking support from counseling services, support groups, or online communities can provide valuable emotional relief and practical advice from others who share similar experiences.
Combining Nonsurgical Treatment Options for Optimal Results for Avoiding Surgery
A combination of non-surgical thyroid eye disease treatment options often provides the best results. For example, patients may use lubricating eye drops alongside corticosteroids or combine radiation therapy with Tepezza infusions.
The right mix of treatments depends on the severity of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and their response to different therapies. A tailored approach, guided by a specialist, ensures that each patient receives the most effective care.
Non-surgical treatment options for thyroid eye disease offer various strategies to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve quality of life. From medications like Tepezza and corticosteroids to lifestyle modifications and supportive therapies, these approaches provide relief for many patients.
The key to successful management lies in early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and regular monitoring by a healthcare team. By exploring and combining these options, patients can take control of their condition and achieve better outcomes.